ü Preparation of Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7): It is prepared by the reaction of chromate ore (FeCr2O4) with sodium carbonate in excess of air.
(i) Conversion of chromite ore to sodium chromate
4 FeCr2O4
+ 8 Na2CO3 + 7 O2 → 8 Na2CrO4
+ 2 Fe2O3 + 8 CO2
(ii)
Acidification
of sodium chromate to sodium dichromate
2Na2CrO4
+ 2 H+ → Na2Cr2O7 + 2 Na+
+ H2O
(iii) Conversion of sodium dichromate to potassium
dichromate
Na2Cr2O7 + 2
KCl → K2Cr2O7 + 2 NaCl
Ø Properties
·
Physical properties:
(i) It forms orange red crystals which
melt at 396 0C.
(ii) It is moderately soluble in
cold water but freely soluble in hot water.
·
Chemical properties:
The chromate and dichromate
are inter-convertible in aqueous solution depending upon pH of the solution. Chromate on acidification gives dichromate and the dichromate
on treating with alkali gives chromate.
2 CrO42–
+ 2H+ → Cr2O72– + H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 2OH- → 2 CrO42– + H2O
The
oxidation state of chromium in chromate and dichromate is +6.
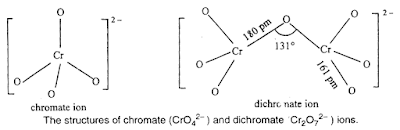
The structures of chromate ion, CrO42– and the dichromate ion, Cr2O72– are shown
below.
Sodium and potassium dichromates are strong oxidising agents. The sodium salt has a greater solubility in water and is extensively used as an oxidising agent in organic chemistry.
o Action of Alkalies: When an
alkali is added to an orange red solution of dichromate, a yellow solution
results due to the formation of chromate.
K2Cr2O7 + KOH → K2CrO4
+ H2O
o Oxidising Properties: K2Cr2O7 is a good
oxidising agent in acidic medium. Its
oxidising action can be represented as follows:
Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Thus, acidified potassium dichromate
will oxidise
1)
Iodides to iodine
6 I – → 3I2
+ 6 e-
![]() Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
6I – + Cr2O72– + 14H+ → 3I2 + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Overall Reaction
2)
Sulphides to sulphur
3S2- →3 S + 6e-
![]() Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
3S2- + Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ → 3S + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
3)
Tin(II) to tin(IV)
3 Sn2+ → 3Sn4+ + 6
e-
![]() Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
3Sn2+ + Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ → 3 Sn4+ + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
4)
Iron(II) (ferrous) to
iron(III) (ferric)
6 Fe2+ → 6Fe3+ + 6 e-
![]() Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72–
+ 14 H+ + 6 Fe2+ → 2 Cr3+ + 6 Fe3+
+ 7 H2O

0 Comments